
WEST NILE FEVER

ABOUT WEST NILE FEVER
West Nile fever is a viral disease caused by the West Nile virus. It is transmitted by mosquitos between humans and animals and can be fatal in horses and birds.
Where does it occur?
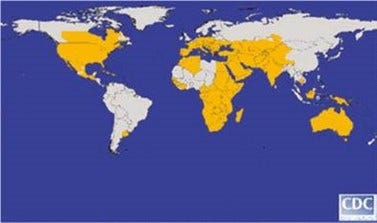
Until recently, West Nile virus outbreaks were limited to Eastern Europe, the Middle East, Africa and West Asia. However, reports in the western world are increasing and a rare subtype of the mosquito virus (Kunjin) has been found in northern and western Australia.
What are the symptoms of West Nile fever?
West Nile virus symptoms are difficult to diagnose and in 80% of cases, display no symptoms at all. If symptoms do show, they display as mild flu. 20% of West Nile virus sufferers will develop West Nile fever symptoms which include:
fever
headache
fatigue
body aches
vomiting
skin rash
swollen lymph glands
What causes West Nile fever?
14 mosquito types carry the West Nile virus, but birds are the natural hosts. A mosquito becomes infected when it bites an infected bird. The virus travels to its salivary glands and is injected into a new host–human or animal–with the mosquito’s next bite.
How do you prevent West Nile fever?
With no human vaccine, the best way to prevent it is to avoid a bite.
Banish breeding grounds
Mosquitos breed in stagnant water. Remove or clean water containers and keep your swimming pool clean. If you have a pond, get fish–they feed on larvae.
Mosquito-proof your property
Pif Paf mosquito killer products will help keep vectors away. In addition to mosquito killer products, place fly screens on windows and doors for extra protection.
Don't dress to attract arthropods
Make sure mosquitos can’t get their fix and cover your skin with long, loose fitted clothing. Apply insect repellent regularly and avoid wearing perfume or aftershave.
How do you treat West Nile fever?
With no cure, treatment for West Nile fever is designed to alleviate any discomfort caused by more severe symptoms.
Sources:http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/bhcv2/bhcarticles.nsf/pages/West_Nile_virushttp://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs354/en/
Disclaimer: The above information is to be used for educational purposes and not as medical advice. Please still take caution and seek a medical professional for further advice in regards to the above, especially if visiting prone areas.


.jpg?width=550&height=309&format=jpg&quality=80)
.jpg?width=550&height=309&format=jpg&quality=80)